Subsea bulk oil-water separation (Annual Report 2021-2022)
During the last year we have worked on determining separation characteristics of water and a model oil (Exxsol D60) with small amounts of crude (spiking). This is done to mimic the separation characteristics of real crude-water mixtures in the pipe separator. Rheology properties of the resulting oil-water emulsion were studied under flowing conditions by using a mini-loop. The results of this study suggest that the Pal & Rhodes rheology model with adjusted equation constants is the most suitable to predict the emulsion viscosity in pipe (Fig. 1). Other properties like separation time and inversion point were also studied.
Our first test campaign was focused on measuring drainage potential curves for a single tapping point in the pipe separator with spiked and un-spiked Exxsol D60 and comparison against a simple numerical model. The drainage potential gives a relationship between the water cut of a stream tapped from the bottom of the pipe versus the water flow rate tapped. This work showed that the main factor affecting the shape of the drainage potential curves is the flow pattern of the oil-water mixture approaching the tapping point. Crude oil spiking reduces considerably the drainage potential for oil continuous regimes (low water cuts). (Fig. 2)
The next experimental campaign was focused on measuring the separation efficiency and water cut ratio for spiked oil for various total flowrates and inlet water-cuts. Two different concentrations of crude oil (e.g., 185 and 400 ppm) were used to observe the effect of crude concentration on the separation characteristics. Flow pattern of liquid-liquid mixture in pipe were determined along the separator. Crude oil spiking significantly reduces the efficiency of the pipe separator for oil continuous regimes (low water cuts).
We had technical meetings with experts from Equinor and Sintef to get advice and design our experimental procedures, to present our results and get feedback.
The experimental rig is ready to run experiments with air in 2022.
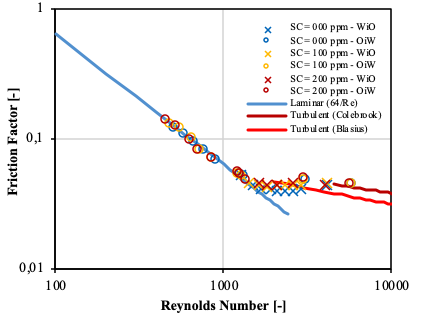
Fig 1 – Emulsion Rheology Model
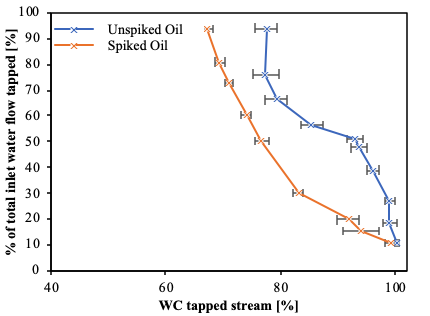

Fig 2 – Drainage Potential Curves Study
No comments
Leave a reply
Cart
Cart is empty.